John Addeo, HackerOne's VP Head of Channels and Strategic Partners , posted on LinkedIn.
What is a Bounty?
What is a Bounty?
In English, “bounty” means a reward. However, in cybersecurity, bug bounty is a program where organizations reward security researchers or ethical hackers for finding and responsibly reporting vulnerabilities in their software, websites, or systems. It helps companies improve their security by leveraging external expertise and fixing issues before they can be exploited.
Through bug bounty programs, companies can apply security patches quickly. Global tech giants such as Google, Apple, Facebook, and Microsoft actively operate such programs to enhance their security. Although South Korea introduced this system in 2012, the number of reports and reward amounts remained low due to a corporate culture hesitant to disclose vulnerabilities and a general lack of security awareness. However, since this year, the system is being increasingly adopted, especially with financial companies launching bug bounty programs under the supervision of the Financial Supervisory Service (FSS), and the Korea Internet & Security Agency (KISA) recruiting joint operators for national bug bounty initiatives.
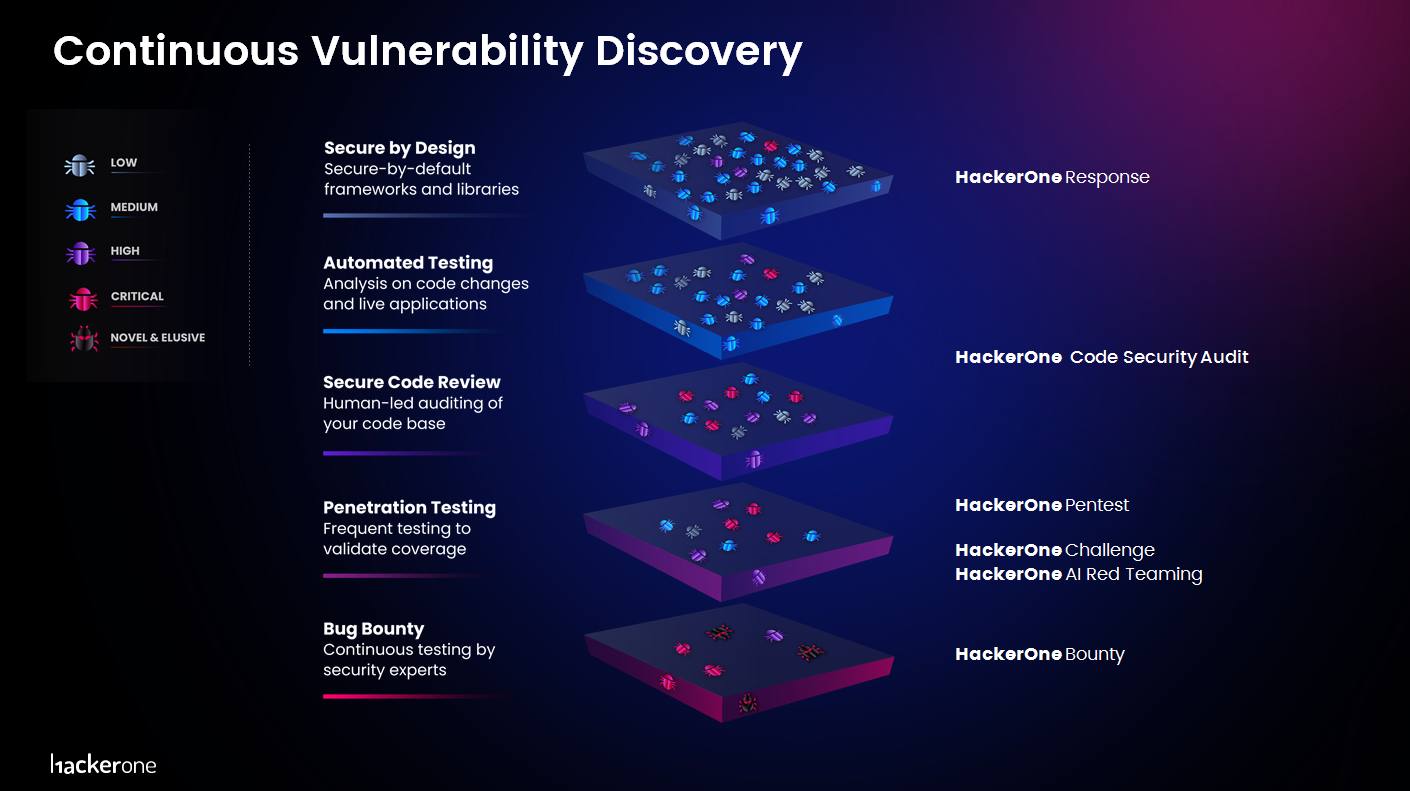
HackerOne is the world’s largest bug bounty platform, with the most reported vulnerabilities and the largest community of ethical hackers. It connects organizations with security researchers to identify and resolve security issues before they can be exploited. Platforms like HackerOne typically charge a platform usage fee, while the bounty itself is directly exchanged between the white-hat hacker and the client.
White-hat hackers participating in bug bounty programs such as HackerOne are thoroughly vetted and act as guardians rather than attackers. Their primary role is to prevent security incidents by identifying and reporting vulnerabilities.